Figure 1: Advanced CNC machining processes bridge the gap between design intent and production feasibility, achieving micron-level precision through digital workflows and automated systems.
Introduction
In today’s competitive landscape, manufacturers across aerospace, medical, and automotive sectors face a perfect storm of challenges: part designs are increasingly complex, tolerance requirements are tighter than ever, and the pressure to shorten time-to-market is immense. Traditional manufacturing methods often create a critical gap between design intent and production feasibility, leading to project delays, cost overruns, and inconsistent quality.
This article delves into how advanced CNC machining processes bridge this gap through digital workflows and precision engineering. We will systematically break down the core technological principles, robust quality assurance systems, and real-world applications that make modern precision manufacturing a reliable strategic asset.
How Do Modern CNC Machining Processes Achieve Micron-Level Precision?
Achieving and maintaining micron-level precision is the cornerstone of advanced manufacturing. It relies on a sophisticated interplay of hardware, software, and control systems.
1. The Foundation: Computer Numerical Control and Servo Drives
At the heart of every CNC machining system is the computer controller that translates digital part designs (CAD models) into precise machine tool movements. Servo drive technology provides the motive force, ensuring each axis moves with exceptional accuracy and repeatability. This closed-loop system constantly monitors position and velocity, making real-time adjustments to maintain the programmed path, which is fundamental for high-precision manufacturing.
2. The Role of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T)
Precision is meaningless without a standardized language to define it. Referencing the ASME Y14.5 standard for geometric dimensioning and tolerancing provides a clear framework for design engineers to communicate functional requirements. Modern CNC machining processes are uniquely capable of meeting these sophisticated GD&T calls, such as true position and flatness, by maintaining a single, stable datum throughout the machining cycle.
3. Thermal Stability and Advanced Metrology
Environmental factors, especially heat, are a significant threat to precision. Leading machine tools incorporate thermal stability technologies, such as cooled ball screws and environment-controlled enclosures, to minimize thermal drift. Furthermore, integration with advanced metrology tools, like on-machine probes, allows for in-process verification, creating a true closed-loop manufacturing system that compensates for any deviations in real-time.
What Are the Critical Differences Between Various CNC Machining Techniques?
Selecting the right CNC machining technology is paramount for efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Each technique offers distinct advantages for specific geometric features.
1. Milling vs. Turning: Choosing the Primary Machining Strategy
The fundamental choice often lies between milling and turning. CNC milling processes involve a rotating tool that moves against a stationary workpiece, ideal for creating complex features like pockets, slots, and 3D contours. In contrast, CNC turning rotates the workpiece against a stationary tool, making it the superior choice for manufacturing rotationally symmetric parts like shafts and fittings. Many complex components benefit from a comprehensive CNC machining processes approach that combines both on a single platform.
2. The Strategic Advantage of Multi-Axis Machining
While 3-axis machining is adequate for simpler parts, multi-axis machining (encompassing 4-axis and 5-axis) is essential for complex geometries. The primary benefit is single-setup machining, which eliminates errors associated with repositioning the workpiece. This not only enhances accuracy but also allows the tool to maintain an optimal orientation to the workpiece, improving surface finish and drastically reducing machining time for intricate components like impellers or medical implants.
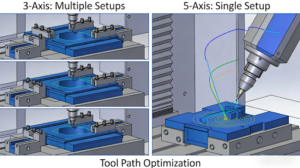
Figure 2: 5-axis CNC technology enables simultaneous movement along multiple axes, eliminating repositioning errors and ensuring high precision for complex parts.
3. Application-Based Selection with Real-World Impact
For instance, a simple bracket might be efficiently produced on a 3-axis mill, while a turbine blade with free-form surfaces demands a 5-axis system. The decision matrix should always consider part geometry, required tolerances, and production volume. This strategic selection is a core component of Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and is critical for project success.
How Does Automated Manufacturing Enhance Production Efficiency and Consistency?
Industrial automation is the engine that drives modern production efficiency, transforming CNC workshops into highly predictable and scalable operations.
- Reducing Human Error and Enhancing Repeatability: By automating material handling, tool changing, and part loading/unloading, automated manufacturing cells drastically reduce human intervention. This minimizes the risk of manual errors and ensures that the ten-thousandth part is identical to the first, achieving unparalleled manufacturing consistency. This is especially critical in regulated industries where traceability and repeatability are mandated.
- Achieving 24/7 Continuous Production: Robotic integration allows for lights-out manufacturing, where machines can operate unattended for extended periods. This maximizes equipment utilization, significantly increases production capacity, and shortens lead times. Studies, including those from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) on smart manufacturing, highlight that automation can boost overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by over 30%, making it a cornerstone of lean production.
- Data-Driven Process Optimization: Automation systems are not just about mechanics; they are data hubs. They collect vast amounts of data on cycle times, tool wear, and machine health. Analyzing this data enables predictive maintenance, preventing unplanned downtime, and allows for continuous process optimization, further driving down costs and improving quality over time.
What Quality Assurance Systems Ensure Reliability in Precision Manufacturing?
Owning advanced machinery is insufficient without a systemic quality assurance framework. Reliability is built on a foundation of rigorous processes and international standards.
1. The Full-Spectrum Quality Control Loop
A robust system covers the entire journey, from incoming raw material certification to final inspection. This includes First Article Inspection (FAI), in-process checks using calibrated instruments, and a final audit against the customer’s drawing requirements. This end-to-end scrutiny ensures that every delivered part meets the specified precision reliability.
2. The Critical Role of ISO and Industry-Specific Certifications
Adherence to international standards is non-negotiable. ISO 9001 certification provides the baseline for a quality management system. For high-stakes industries, specific standards like AS9100D for aerospace and ISO 13485 for medical devices impose stricter controls for risk management, traceability, and validation. These certifications provide customers with verifiable evidence of a manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
3. Documentation and Traceability as a Value Proposition
For every component, especially in regulated sectors, full data traceability is required. This means documenting material certifications, inspection reports, and machine settings for each batch. This level of documentation is not just a compliance activity; it is a powerful tool for root cause analysis and continuous improvement, ensuring that ISO-certified manufacturing delivers on its promises.
How Can Manufacturers Select the Right CNC Machining Partner for Critical Applications?
Choosing a manufacturing partner is a strategic decision. The right partner acts as an extension of your engineering team, while the wrong one can jeopardize your project.
- Evaluating Technical Capabilities and Technology Stack: The assessment must go beyond basic machine lists. Look for a partner with a modern technology stack that includes multi-axis machining capabilities, advanced metrology equipment (like CMMs), and proficiency with the latest CAD/CAM software. Their technical expertise should align with your industry’s specific challenges, whether it’s machining high-temperature alloys for aerospace or biocompatible materials for medical devices.
- Assessing Quality Culture and Communication: Technica: l capability must be matched by a deeply ingrained quality culture. During evaluations, review their quality manuals, audit reports, and inspection protocols. Equally important is their responsiveness and communication style. A partner that provides clear Design for Manufacturability (DFM) feedback early in the design stage demonstrates a proactive approach that prevents costly errors down the line.
- The Importance of Industry Experience and Project Management: Finally, seek a partner with proven experience in your field. They will understand the unspoken requirements and regulatory hurdles. Effective project management is also critical, ensuring timelines are met, and you are kept informed throughout the production process. Selecting a true partner, rather than just a vendor, is the final step in leveraging professional CNC machining services for success.
What Are the Emerging Trends in Smart Manufacturing and Digital Fabrication?
The future of manufacturing is digital, connected, and intelligent. Advanced production techniques are evolving rapidly, offering new levels of efficiency and flexibility.
1. The Rise of Industrial IoT and Digital Twins
Smart manufacturing leverages the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), where machines are equipped with sensors that generate real-time data on performance and health. This data fuels the creation of digital twins — virtual replicas of physical systems. Engineers can simulate and optimize production processes in the digital realm before executing them in the real world, reducing waste and accelerating innovation.
2. Adaptive Machining and AI-Driven Optimization
Moving beyond pre-programmed paths, adaptive machining systems use in-process sensor data to dynamically adjust cutting parameters. This compensates for variables like tool wear or material inconsistencies, ensuring consistent quality. Furthermore, Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms are beginning to analyze manufacturing data to optimize toolpaths and predict failures, pushing the boundaries of production efficiency.
3. Sustainability and Additive/Subtractive Hybridization
Digital fabrication is also becoming more sustainable. There is a growing focus on optimizing material usage and energy consumption. A significant trend is the hybridization of additive manufacturing (3D printing) for creating complex near-net shapes and CNC machining for achieving final precision, combining the design freedom of one with the accuracy of the other.
Conclusion
Advanced CNC machining processes have fundamentally transformed modern manufacturing from a craft into a high-tech discipline. By integrating digital design data with automated, precision-driven execution, these technologies effectively solve the core challenges of complexity, precision, and time-to-market. A robust quality assurance system, underpinned by relevant certifications, ensures that this precision reliability is consistent and dependable. As smart manufacturing and digital fabrication trends continue to evolve, they promise even greater levels of efficiency and innovation for businesses that embrace them.
FAQs
Q1: What is the typical lead time for CNC machined prototypes?
A: Standard prototype lead times typically range from 3-5 business days for most materials and complexities. However, this can vary based on part size, material availability, and specific geometric requirements. Factors such as complex internal features or tight tolerances below ±0.01mm may extend the timeline. Many manufacturers offer expedited services for urgent projects.
Q2: How do ISO certifications impact manufacturing quality?
A: ISO certifications establish systematic quality management frameworks that ensure consistent output. They mandate documented procedures, regular audits, and continuous improvement cycles. For manufacturers, this means reduced variability and better process control. For customers, it provides assurance of reliable quality and reduced risk.
Q3: What materials are most suitable for high-precision CNC machining?
A: The material selection depends on application requirements. Commonly used materials include aluminum alloys (good machinability), stainless steels (durability), titanium (high strength), and engineering plastics like PEEK. The choice should consider factors like mechanical loads, operating environment, and regulatory requirements.
Q4: How does 5-axis CNC machining differ from 3-axis for complex parts?
A: 5-axis CNC machining provides significant advantages by allowing simultaneous movement along five different axes. This enables single-setup machining of complex surfaces, reducing cumulative errors and improving accuracy compared to 3-axis processes that require multiple repositioning. It achieves better surface finish and shorter production times for intricate components.
Q5: What design considerations are crucial for successful CNC machining?
A: Key design for manufacturability considerations include appropriate wall thickness (minimum 0.5mm for metals), proper corner radii, and attention to feature accessibility for cutting tools. Avoiding unnecessarily tight tolerances where not functionally required can significantly reduce manufacturing costs and improve production efficiency.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing expert at LS Manufacturing, a company that helps engineers and researchers solve complex part challenges in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. With a commitment to quality assurance and advanced CNC machining processes, the team ensures high-quality solutions. For more insights, contact them today for a free, no-obligation project review and DFM analysis.
