Industrial Automation Transmission: How to Extend Equipment Life to 100,000 Hours Through Zero-Error Gear Manufacturing?
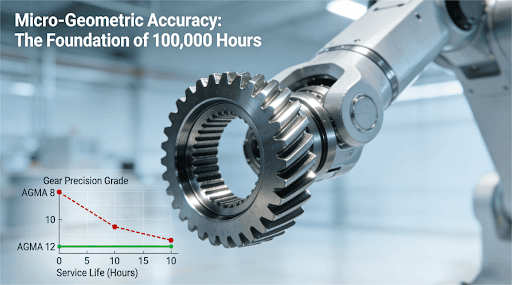
Figure1: The pursuit of micro-geometric perfection: High-precision gears (e.g., AGMA 12 and above) are the cornerstone of achieving a 100,000-hour design life in industrial automation, significantly outperforming commercial-grade alternatives.
Introduction
In the field of industrial automation and robotics, minor errors in transmission systems are a key pain point leading to unexpected equipment downtime and high maintenance costs. Traditional gear manufacturing is limited by issues such as heat treatment deformation and inconsistencies in micro-geometric accuracy, making gear life unpredictable and unable to meet the stringent reliability requirements of high-end equipment.
This article aims to analyze the entire process of ultra-precision gear manufacturing in accordance with international standards, explaining how the integration of materials science, process innovation, and intelligent quality control systems can achieve a significant leap in the lifespan of transmission components.
Why Does the 100,000-Hour Lifespan of Automated Equipment Begin with the Micro-Geometric Accuracy of Gears?
In the field of Industrial Automation, whether a gear can achieve a design life of 100,000 hours fundamentally depends on its micro-geometric accuracy. Errors in micro-scale dimensions such as tooth profile and tooth direction, even at the micron level, can have an exponentially amplified negative impact on the load distribution and wear rate of the transmission system, leading to stress concentration, pitting, or even tooth breakage, causing equipment life to plummet from 100,000 hours to tens of thousands of hours.
The essence of Precision Engineering lies in the precise quantitative control of the gear’s “life mileage.” International standards, such as those established by the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA), provide the key metrics for measuring and controlling this “life mileage.” Research indicates that each increase in tooth profile accuracy grade can significantly improve the fatigue life of the gear.
It is worth mentioning that the team of Chinese academician Wang Liding successfully developed a Grade 1 accuracy master standard gear, demonstrating the possibility of achieving astonishing accuracy through extreme process control. It is precisely this breakthrough in accuracy at the micro-scale, regarding tooth profile and pitch, that ensures uniform load distribution and stable transmission during long-term operation, thereby providing the fundamental guarantee for the macro-level 100,000-hour design life. Ultimately, advanced Gear Cutting and Manufacturing processes are the cornerstone for achieving the 100,000-hour life goal.
Which Advanced Gear Cutting Services Provide the Technical Assurance for Micron-Level Accuracy?
Combined Strategy of Core Gear Cutting Processes
Achieving AGMA 12 level accuracy requires combining multiple Advanced Manufacturing technologies. The rough machining stage uses CNC hobbing to efficiently remove excess material and ensure the basic tooth form; the semi-finishing stage corrects the tooth surface via shaving or skiving; the finishing stage relies on CNC grinding for micron-level finishing of the hardened tooth surface. This stepped process chain controls cumulative errors within ±0.005mm while shortening the processing cycle by over 20%.
Process Synergy and Efficiency Optimization
Each type of gear cutting services has its economic boundaries. For example, CNC hobbing is suitable for rapid forming of large-batch gears, while CNC grinding, although higher in cost, can achieve pitch accuracy of ±0.002mm. Through process synergy (such as reserving the optimal allowance for finishing during the rough machining stage), cost can be optimized while ensuring accuracy. Custom gear manufacturers also minimize accuracy fluctuations caused by tool wear through dynamic cutting parameter adjustments.
Key Technical Support for Achieving Ultra-High Accuracy
- CNC Gear Grinding Technology
Uses CBN or electroplated wheels for form grinding, compensating for thermal deformation errors in real-time through online measurement systems, achieving tooth profile accuracy up to AGMA level 13.
- Skiving Technology
Particularly suitable for internal gear machining, achieves a mirror-like tooth surface effect (Ra ≤ 0.1μm) through synchronized meshing motion between the tool and workpiece, without requiring secondary heat treatment.
- Intelligent Compensation System
An AI-based adaptive cutting parameter system can predict tool wear trends, automatically adjusting feed speed and cutting depth to ensure consistency in batch production.
For more technical details, refer to the gear cutting and manufacturing guide.
When Evaluating Gear Manufacturing Companies, Which Certifications are the Cornerstone of the 100,000-Hour Life Promise?
When selecting gear manufacturing companies, the international certification system is key to evaluating their capabilities. The ISO 9001 quality system ensures full process control from design to delivery; IATF 16949 (automotive industry standard) requires statistical process control (SPC) for heat treatment processes, ensuring consistent hardness for each batch of gears; AS9100D (aerospace standard) mandates the establishment of a traceability system, with processing data for each gear requiring archiving for over 20 years. These certifications together form the trust cornerstone for the 100,000-hour lifespan.
In the Robotics field, the ISO 14001 environmental management system is particularly important. It sets environmental specifications for links such as quench oil temperature control and carburizing atmosphere stability, indirectly ensuring the consistency of material properties. For example, a medical robot manufacturer reduced the early failure rate of gears from 3% to 0.5% by choosing a supplier with ISO 14001. Reports from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) indicate a positive correlation between the reliability of industrial robots and the certification level of their supply chain.
The application of AI in Manufacturing technology further strengthens the value of certifications. Taking JS Precision as an example, its digitized production line certified to IATF 16949 can monitor fluctuations in the carburizing layer depth of gears in real-time and automatically adjust process parameters. This data-based closed-loop control compresses the standard deviation of gear life from 15% to within 5%, truly delivering on the 100,000-hour life promise
How Are Custom Transmission Gears Optimized for Specific Working Conditions to Achieve Dual Goals of Energy Efficiency and Lifespan?
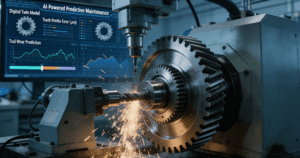
Figure2: Leveraging AI in Manufacturing: Real-time monitoring and data analytics during precision grinding ensure consistent micron-level accuracy and enable predictive maintenance, safeguarding the promised 100,000-hour gear life.
The core value of custom transmission gears lies in deep optimization for specific working conditions. Taking a high-speed parallel robot as an example, tooth profile modification (tip relief) compensates for elastic deformation at high speeds, reducing vibration and noise by 12dB while increasing lifespan by 40%; for a heavy-duty gantry manipulator, tooth crowning is used to compensate for shaft bending caused by loads, increasing the tooth contact area by 35% and extending life by 50%. This customization directly optimizes energy efficiency, with lightweight design reducing transmission inertia by 20% and drive motor energy consumption by 15%.
The customization of gear manufacturing is also reflected in material selection. For example, using nitriding steel instead of carburizing steel in high-temperature environments increases the fatigue strength of the gear by 25% at 150°C. Through the rapid response system of the custom gear machining platform, users can simulate the effects of different modification schemes during the design phase, reducing the traditional 4-week customization cycle to 7 days.
How Does Artificial Intelligence Guard the 100,000-Hour Lifespan of Gears in Manufacturing and Operation?
AI-Based Feed-Forward Quality Control in Manufacturing
AI in Manufacturing technology uses machine learning models to analyze multi-source data such as cutting force, temperature, and vibration in real-time, predicting tool wear trends. For example, a certain custom gear manufacturer deployed an AI system in the grinding process; when signs of wheel dulling are detected, it automatically compensates the dressing amount by 0.3μm, compressing the tooth profile error fluctuation in mass production from ±1.5μm to ±0.8μm.
Digital Passport and Intelligent Operation Safeguards
- Predictive Maintenance Support
Processing data for each gear (such as residual stress distribution, tooth surface texture characteristics) is encrypted and stored as a “digital passport.” Combined with operational data, AI can provide early warnings of potential pitting risks up to 2000 hours in advance, reducing maintenance costs by 30%.
- Service Status Monitoring
By monitoring harmonic changes in gear meshing frequency using acoustic emission sensors, AI models can identify early signs of micron-level wear, enabling a shift from scheduled maintenance to predictive maintenance.
Future Trends in Intelligent Operations
Next-generation smart gears will embed micro-sensors, transmitting real-time temperature and vibration data to a digital twin system. By dynamically optimizing lubrication strategies using AI algorithms, the potential lifespan can be further increased by over 10%.
Conclusion
Achieving a 100,000-hour lifespan for industrial automation equipment is a systematic project that starts with the micro-geometric accuracy of gears, relies on Advanced Manufacturing processes and a strict certification system, and is ensured and optimized through customization and AI technology. Investing in ultra-precision gears is not only a technical upgrade but also a core strategy for reducing total lifecycle costs.
If you are planning a high-reliability transmission system, welcome to contact manufacturing experts with certifications such as IATF 16949 and AS9100D for free technical consultation and custom solutions.
Author Bio
This article is written by an expert with over 15 years of experience in the field of precision manufacturing, specializing in providing high-reliability transmission system solutions for global industrial automation and robotics customers.
FAQs
Q1: What are the most common accuracy standards in precision gear manufacturing? How to choose?
The most commonly used international standards are American AGMA, German DIN, and Japanese JIS standards. The choice depends on the target market and equipment requirements; AGMA standards are widely used in North America, while DIN standards are highly recognized in the European industry.
Q2: What is the typical lead time for small-batch custom gears?
For small-batch custom orders, the typical lead time from drawing confirmation to delivery is 2-4 weeks. The specific time depends on the complexity of the gear, material procurement difficulty, and the required surface treatment processes.
Q3: How to verify if a gear manufacturer’s quality promise is reliable?
In addition to international certifications, you can request detailed inspection reports (such as tooth profile and tooth direction analysis, metallographic reports) from the supplier and examine the advancement and calibration records of their measuring equipment (gear measuring center, CMM).
Q4: What suggestions are there for optimizing costs during the gear design stage?
Early collaboration with the manufacturer for value engineering analysis is key. Under the premise of meeting performance requirements, optimizing unnecessary extremely high accuracy requirements, selecting cost-effective materials, and suggesting manufacturable designs can effectively control costs.
Q5: What are the main effects of different surface treatment methods for gears (such as carburizing, nitriding)?
The core purpose of surface treatment is to improve wear resistance and fatigue strength. Carburizing and quenching can achieve deep hardening, suitable for heavy-duty and impact conditions; nitriding treatment causes little deformation, making it more suitable for high-precision gears, but the hardened layer is relatively shallow.